Batch Upscale Images with Topaz Gigapixel AI: Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction
Gigapixel AI by Topaz Labs is a great tool that can both enlarge/upscale your images AND increase image quality.
Gigapixel AI is a staple tool in my image post-processing workflow. I consistently use it to upscale my MidJourney AI images and have also used it for enlarging my photography for prints.
Images can be upscaled at 2x, 4x, 6x, and higher. Not only are images larger, but the quality is improved over the original input.
One of the best features of Gigapixel AI, in my opinion, is batch upscale processing.
If you have a lot of images that need to be enlarged, doing this one by one is painful (been there, done that). Being able to batch upscale images allows you to set it up, walk away, and let it do its thing.
In this article, I will share a step-by-step tutorial of how to batch upscale images with Topaz Labs Gigapixel AI.
Note: FREE TRIAL versions are available for all of the Topaz Labs tools here.
View system requirements here.
For a step-by-step guide to upscaling MidJourney AI images with Topaz Labs Gigapixel AI, you can check out this article.
Disclosure: This post contains some affiliate links. If you decide to make a purchase through my links, I will get a small commission at no cost to you. Any commissions directly support upkeep of this website.
1. Open Topaz Labs Gigapixel AI
If you already have Gigapixel AI, then this step is easy.
If you don't, download and install the FREE TRIAL of Topaz Labs Gigapixel AI. Upon launching Gigapixel AI for the first time, you will be prompted to download the AI models that it needs. Downloading the models can take a few minutes, depending on your internet connection, but the process is straightforward.
2. Drag and drop your images into Gigapixel AI
Next, drag and drop your images or folder of images into the Gigapixel AI window. A scrollable list of your images will appear at the bottom of the window. You can click any image in the list to view it in the main view, where you will be able to try different AI models and settings.
3. Select your Resize Mode
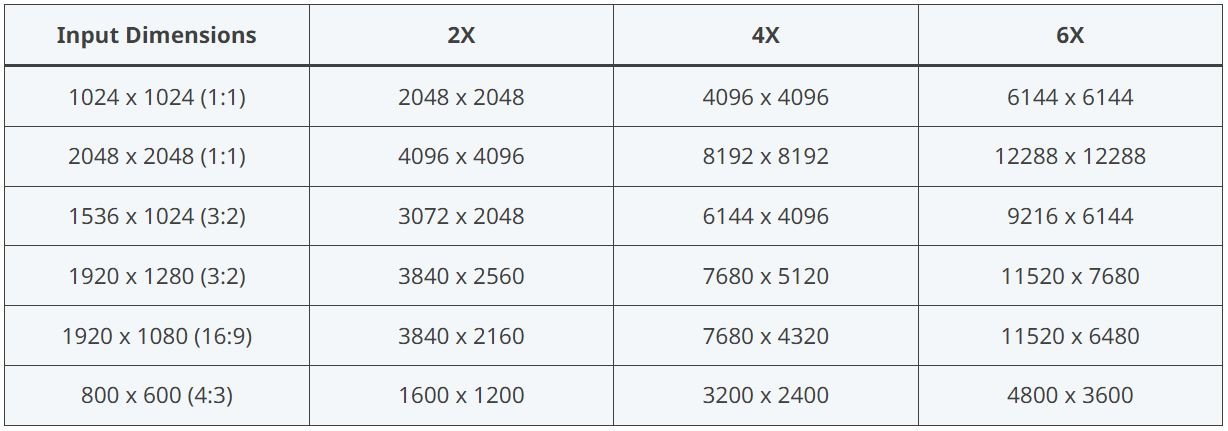
With Gigapixel AI, you have a lot flexibility in how you define your output image size. You can select one of the 0.5x, 2x, 4x, or 6x buttons to specify how many times larger (based on the image's current dimensions) you want the output image to be. 2x is 200% larger, 4x is 400% larger, 6x is 600% larger, etc.
I typically select 4x. This means a 1024x1024 pixel image would be increased to 4096x4096 pixels.
They also have a "..x" button where you can specify how many x larger. However, anything larger than 6x and you run the risk of losing image quality.
If you want to specify exact output dimensions and pixels per inch (ppi/dpi), click on either the Width or Height button. Type in what you want your output width or height to be (inches, pixels, or centimeters). Then type in the number of pixels/inch or pixels/centimeter the output image should have.
4. Pick an AI model
Gigapixel AI offers the following AI models: Standard, Lines, Art & CG, HQ, Low Res, and Very Compressed. Each model is designed for different styles and quality of input images.
For photography, Standard and HQ are great choices. For AI generated images, such as those made with MidJourney, I find that the Art & CG model works best.
If you aren't sure which model you want to use for your images, I highly recommend utilizing the Comparison View feature. Comparison View allows you to compare four AI models at once. To activate Comparison View, click the icon in the upper right, just to the left of the magnifying glass.
Once Comparison View is enabled, you will see four quadrants. Each quadrant shows a different AI model on your image. To change which AI model is used in each quadrant, simply click one of the quadrants and then click an AI model from the set of models on the right side of the window. You can do this for all four quadrants.
Play around and see what works best for your images.
5. Adjust the settings
After you decide on an AI model, switch your view to either the Side-by-Side View or Split View. Make sure the AI model you've chosen, is selected on the right.
Next, make any adjustments to the Settings panel on the right. You can increase noise suppression, reduce blur, fix compression, turn on face recovery (if your images have faces), and gamma correction.
For AI generated images, I typically use low values for Suppress Noise, Remove Blur and Fix Compression. I turn on Gamma Correction, because I find that it can help to improve overall image clarity.
Want to set different AI models for different images in your batch?Click here to learn how.
6. Save your images
We've made it to the final step!
Click the "Save Images" button in the lower right.
Gigapixel AI has 6 different image formats available: JPG, JPEG, TIF, TIFF, PNG, and DNG. Depending on which image format you select, you can customize quality, color profile, compression, and bit depth.
Lastly, set a custom filename and output folder (if you want), and click Start!
Note: If you are using the FREE TRIAL, you will NOT be able to save your images unless you purchase the program. I recommend trying it out with several images and deciding for yourself.
After you click Start, you will see a table-style view of all of the images being upscaled. The multiple columns of information contain your input image dimensions, amount of upscale, what the final output dimensions will be, the AI model used, and any custom settings.
How long does batch AI upscaling with Gigapixel AI take? That depends on your computer specs, the size of your input images, how large the upscales are, (possibly) the AI model, and if the images are stored locally. Click here for my rough time estimates.
Batch upscaling processing
Notes on processing speed and using multiple AI models
Gigapixel AI batch processing speed: How fast is it?
In my testing, I noticed that batch processing speed was affected by the size of the upscale (e.g. 2x vs 6x) and whether my input and output images were local to my PC or on a network drive. Larger upscales took longer. Images being accessed from or saved to a network drive also made the processing take longer.
For example, batch processing 12 images (dimensions range 1-4.2 MP) at 2x upscale locally took about 9.25 seconds per image. Batch processing the same 12 images locally at 4x upscale took about 17 seconds per image. Batch processing the 12 images at 4x from and to a network drive took about 24.4 seconds per image.
I suspect the processing speed could also be affected by AI model and size of the input image, but I did not explicitly test these.
Results will vary, but the takeaways are:
Expect several seconds per image. If you have thousands of photos to upscale, set it up to run overnight.
The larger the upscale is, the longer the image will take to process
Storing and saving images locally (when batch processing) will speed up the process
PC Specs Used:Processor: Intel i7 10700K, Memory: 32 GB, Graphics: Radeon RX 570
Can you use different AI models for different images when batch upscaling with Gigapixel AI?
Yes.
At the bottom of the window where your scrollable list of images is, you'll see a "Select All" button. By default, all images are selected. Any change you make to your settings will thereby apply to all of your images. If you want to do something different for a single image, uncheck "Select All" and select the image you want to use different settings. You can change any of the settings for the image you've selected, including the AI model and Resize Mode.
From here, you can move on to edit the settings for another single image. I do not recommend clicking "Select All" at this point, because any changes made after re-checking "Select All" will wipe out the individual image settings changes you made.
Summary
In summary, batch processing images in Topaz Labs Gigapixel AI enables you to quickly upscale large numbers of images.
You can select from several AI models to choose the one that works best for your images.
The program not only upscales your images, but it also improves the overall image quality.
Gigapixel AI is user-friendly and a valuable tool to any post-processing workflow that requires image enlargement.
If you found this article helpful and informative, please consider sharing it and leaving a comment! Thanks for reading!